 Scan and follow WeChat
Scan and follow WeChat
In international trade, logistics is an indispensable step. Doing a good job in international logistics and holding the goods in your own hands firmly shall help you have no fear to lose them.
So we need to understand more clearly on the ways of international logistics. On the one hand, we can ensure the safety of the goods, on the other hand, we can have the goods timely delivered to customers through these ways, which means that we can recover the payment for goods at an earlier date and avoid difficulties in capital turnover.
The following focuses on the introduction of several international shipping delivery methods and differences:
TELEX RELEASED:
Definition: Short for Telex Release B/L. The information of bill of lading is sent to the shipping company at the port of destination by electronical data file or electronic message. The consignee can get the bill of lading and take the goods by means of telex release copy with telex release seal and telex release guarantee letter. The shipping company informs the destination port agent to release the goods, without the original bill of lading, as long as someone proves that he is the consignee and whom the telex releasee is sent to, he can take the goods.

Advantages: convenient, fast, safe (avoid the risk of losting bill of lading).
Disadvantages: The shipper no longer have the property right after sending a txtel release.
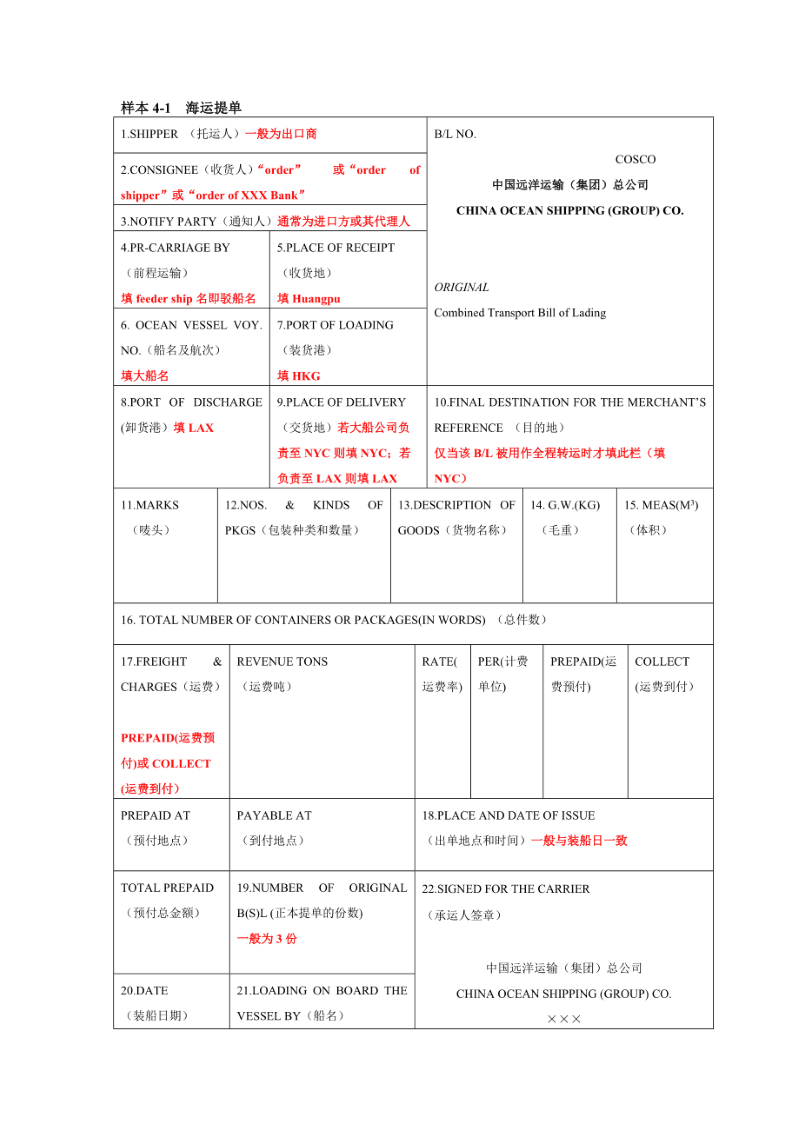
OCEAN BILL (B/L) :
Definition: Original bill of lading issued by shipping company. It is a kind of certificate of property right, according to which the consignee takes the goods, it can endorse the transfer, is an important document; The SHIPPER will get the original B/L from the forwarder, scan it to CNEE, and arrange payment. The SHIPPER will send the whole set of B/L by express mail to CNEE, who can exchange it to the original B/L to pick up the goods. Ocean bill of lading is used more.
Advantages: It is convenient for the buyer to take delivery of goods immediately, simplified procedures, save costs.
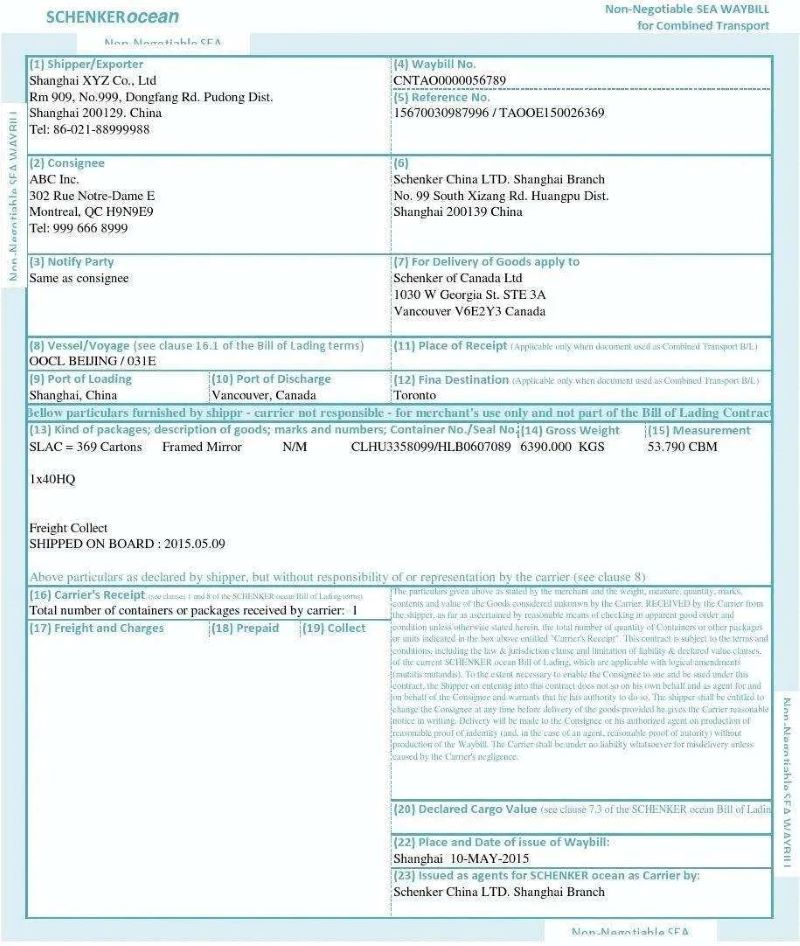
SWB (Sea Waybill) :
Definition: Short for SEA WAYBILL, it is a form of bill of lading release. Once you get out of SWB, the cargo right will be transferred from SHIPPER to CNEE, that is to say, CNEE can pick up the goods directly, SWB pick up the goods does not need the original copy, and there is no need for telex release fee. For trusted companies, this release form can be adopted.
Advantage: the order is quick, quick delivery, convenient, fast.
Disadvantages: There is generally no way to control the cargo.
Application Scenario:
1. The shipping waybill can be shipped after receiving the payment in full.
2. Multinational companies, whose subsidiaries in China are specialized in purchasing goods for foreign parent companies, can quickly go to sea waybills in order to facilitate delivery.
Port of destination Release:
Definition: The meaning of releasing goods. This mode is rarely used. It will be used in the following special circumstances: if the B/L is lost, the consignor will write the letter of guarantee to the shipping company or the agent,who will release the goods to the consignee; The bill of lading is late, and the goods arrive, in order to pick up the goods earlier, you can also take the letter of guarantee instruction to release the goods.
Application scenario: This method is generally not used in the absence of special circumstances.
The differences:
1. SWB is a shipboard BILL of lading, which is similar to telex release. Once the SEA WAY BILL is confirmed, the agent will directly release the goods to the consignee after the goods arrive at the port.
2. Telex release, even if the goods have been at the port for a long time, as long as the consignor has not notified the agent of the release in written form, the agent will not release the goods to the consignee.
3. The main difference between SWB and B/L is that SWB does not have the function of certificate of cargo right. Bill of lading is a kind of certificate of caargo right, which can be transferred by endorsement (indicative bill of lading).
Conclusion
All trades are, in the final analysis, transactions between buyers and sellers. As long as the payment of the customer is received, the above forms of delivery are all free of risk.
